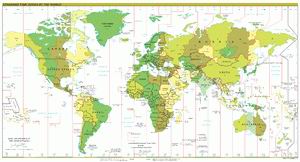
Australia Time World time zone Map
Australia Time Zone and Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Time Zone
- Australia uses three main time zones:
- Australian Western Standard Time (AWST UTC/GMT+08:00)
- Australian Central Standard Time (ACST UTC/GMT+09:30)
- Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST UTC/GMT+10:00)
2022 DST
- Sunday, 3 April 2022, 03:00:00 - Daylight Saving Time End.
- Sunday, 2 October 2022, 02:00:00 - Daylight Saving Time Start.
| Australia Time Zone | Start of DST | End of DST |
|---|---|---|
| Western Australia, GMT+8 | ||
| Queensland, GMT+10 | ||
| Northern Territory, GMT+9.5 | ||
| South Australia, GMT+9.5 | ||
| New South Wales, GMT+10 | ||
| Australian Capital Territory, GMT+10 | ||
| Victoria, GMT+10 | ||
| Tasmania, GMT+10 | ||
Daylight Saving Time (DST) Summer Time
Observance as of 2022
| Country | DST start | DST end |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Mar. 13,(Sun) 02:00 am | Nov. 6,(Sun) 02:00 am |
| Canada | Mar. 13,(Sun) 02:00 am | Nov. 6,(Sun) 02:00 am |
| Europe | Mar. 27,(Sun) 01:00 am | Oct. 30,(Sun) 01:00 am |
| Mexico | Apr. 3,(Sun) 02:00 am | Oct. 30,(Sun) 02:00 am |
| New Zealand | Sep. 25,(Sun) 02:00 am | Apr. 3,(Sun) 03:00 am |
| Australia | Oct. 2,(Sun) 02:00 am | Apr. 3,(Sun) 03:00 am |
Summer Time Is Daylight Saving Time
- Daylight saving time (DST), also known as daylight savings time or daylight time (United States and Canada),
- Summer Time, (United Kingdom, European Union, and some others),
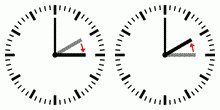 Daylight saving time and summer time is the practice of advancing clocks (typically by one hour) during warmer months so that darkness falls at a later clock time. The typical implementation of DST is to set clocks forward by one hour in the spring ("spring forward") and set clocks back by one hour in autumn ("fall back") to return to standard time. As a result, there is one 23-hour day in late winter or early spring and one 25-hour day in the autumn.
Daylight saving time and summer time is the practice of advancing clocks (typically by one hour) during warmer months so that darkness falls at a later clock time. The typical implementation of DST is to set clocks forward by one hour in the spring ("spring forward") and set clocks back by one hour in autumn ("fall back") to return to standard time. As a result, there is one 23-hour day in late winter or early spring and one 25-hour day in the autumn.
Daylight saving time (DST) in the world
- United States and Canada - daylight saving time starts on the second Sunday in March and ends on the first Sunday in November, with the time changes taking place at 2:00 am local time. With a mnemonic word play referring to seasons, clocks "spring forward, fall back" - that is, in springtime the clocks are moved forward from 2:00 a.m. to 3:00 a.m. and in fall they are moved back from 2:00 a.m. to 1:00 a.m. Daylight saving time lasts for a total of 34 weeks (238 days) every year, about 65% of the entire year.
- Most areas of the United States and Canada observe daylight saving time (DST), the exceptions being Arizona (except for the Navajo, who do observe daylight saving time on tribal lands), Hawaii, and the overseas territories of American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the United States Virgin Islands. The Uniform Time Act of 1966 established the system of uniform daylight saving time throughout the US.
- Europe - in all locations in Europe where summer time is observed (the EU, EFTA and associated countries), European Summer Time begins at 01:00 UTC/WET (02:00 CET, 03:00 EET) on the last Sunday in March and ends at 01:00 UTC (02:00 WEST, 03:00 CEST, 04:00 EEST) on the last Sunday in October each year; i.e. the change is made at the same absolute time across all time zones.
- Russia - Observed DST in 1917–1919, 1921 (some areas), and 1981–2010. In 2011–2014, used permanent DST. In 2014, left permanent DST and switched to permanent standard time.
- Brazil - Observed DST in 1931–1933, 1949–1953, 1963–1968, and 1985–2019.
- Australia - Daylight saving starts each year at 02:00 am on the first Sunday in October, and ends at 03:00 am on the first Sunday in April.
- New Zealand - Daylight saving starts each year at 02:00 am on the last Sunday in September, and ends at 03:00 am on the first Sunday in April.
GMT: Greenwich Mean Time
- Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon; as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. The term 'GMT' is also used as one of the names for the time zone GMT+00:00.
- Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt, noon (12:00:00) GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Greenwich Meridian and reaches its highest point in the sky there. This event may occur up to 16 minutes before or after noon GMT, a discrepancy described by the equation of time. Noon GMT is the annual average (i.e. "mean") moment of this event, which accounts for the word "mean" in "Greenwich Mean Time".
- The daily rotation of the Earth is irregular and has a slowing trend; therefore atomic clocks constitute a much more stable timebase.
- On 1 January 1972, GMT as the international civil time standard was superseded by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
The Difference Between GMT and UTC
- Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is often interchanged or confused with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). But GMT is a time zone and UTC is a time standard.
- GMT is a time zone officially used in some European and African countries. The time can be displayed using both the 24-hour format (0 - 24) or the 12-hour format (1 - 12 am/pm).
- UTC is not a time zone, but a time standard that is the basis for civil time and time zones worldwide. This means that no country or territory officially uses UTC as a local time.